Configuring the Data Sources
Environments and Data Sources
The description given to a data source created for the first time is used throughout the environments to describe this specific data source.
Give a generic description for the first time (e.g., ERP Data Source, Cube Data Source) and if necessary, rename it after the first environment has been created.
The following information is needed to configure the data sources:
- Database server credentials: Server name, Instance, Authentication strategy.
- Main ERP database information: Database and schema name.
- Users: Make sure to have created SQL or Oracle users beforehand.
ERP Data Source
-
In the upper-right hand corner, click on the
to access the Administration section.
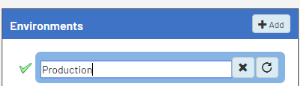
- On the left pane, select Env. & Data Sources.
-
By default, there is already an environment called Production, which you can rename by double-clicking in the name box. Once changed, press the Enter key.
-
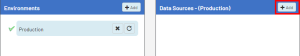
In the Data Sources section, click
Add to create the first data source.
-
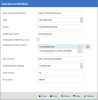
Complete the ERP Data Source configuration. See instructions for MS SQL Server below.
- Click Validate and then Save to complete the configuration of the data source.
| ERP Data Source Fields for SQL Server | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Source Description | Sage 1000 Data Source |
| Type | SQLSERVER |
| Server | Database server of the data warehouse where Sage 1000 has been synchronized in the DataSync configuration. |
| Database Name |
Name of the data warehouse where Sage 1000 has been synchronized in the DataSync configuration (beware of the case sensitivity). |
| Database Schema Name |
Create the two following entries by clicking on the DatabaseName.dbo DatabaseName.SEI_CUSTOM_SCHEMA (replace CUSTOM_SCHEMA with the schema name) Note
The second line contains the SEI Custom Schema. We highly recommend following this naming convention:
Note
The application searches for tables in the same order as the schemas are listed. As soon as a table is found in a schema, the application stops searching. Therefore, if you have multiple tables with the same name in different schemas, make sure that the schema containing the table you want to use appears first. Important
Choose a unique Custom Schema name for each environment. |
| SEI schema |
Enter SEI_CUSTOM_SCHEMA (replace CUSTOM_SCHEMA with the schema name) |
| Authentication Strategy | UseSpecific |
| User Name |
Name of the SQL user accessing the data warehouse. For example, sa. This is the same user you created in Creating SQL Users . |
| Password | The user's password. |
Cube Data Source
In the same environment as the ERP data source, create a new data source for the OLAP Cube.
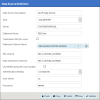
Complete the Data Source Definition with all the appropriate information.
| OLAP Data Source Fields for SQL Server | Description |
|---|---|
| Server | Database server where the SEIOLAP For SQL Server package is installed. |
| Database Name | SEICube. |
| Database Schema Name |
SEICube.SEI_FOLDER (replace FOLDER by the folder name). Where SEI_FOLDER (replace FOLDER by the folder name) is the schema used in the ERP Database of the same environment. |
| SEI schema | Enter the chosen custom schema for the current environment. |
- Click Validate and then Save.
- Click Set as Data Warehouse to define the data source as a data warehouse.
-
Enter the following information:
-
Database warehouse schema: Enter the chosen SEI custom schema again.
-
Use MARS during the cube loading: Unchecked.
-
-
Click Validate and then Save.
Refer to Environments and Data Sources in the Administrator section for more details about the MARS option .