Azure Single Sign-On for Excel Add-in
Single Sign-On (SSO) adds more security and convenience when signing on to SEI Excel Add-in using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
This topic describes how to set up Azure with the SEI Excel Add-in.
Configuring the Azure Domain
You must first configure the Azure Domain, as this is the platform from which we retrieve the data required to correctly set up Excel Add-in.
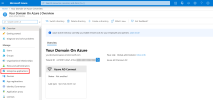
- In your Web browser, go to https://portal.azure.com/ and enter your login credentials (if required).
-
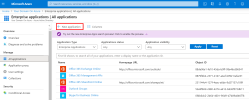
In the left menu, click on Enterprise Applications.
-
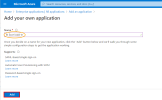
In the upper bar, click on + New application.
-
Under the Add your own app section, select Non-gallery application.
-
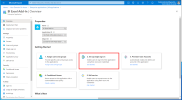
In the Name field, enter a name for your application and click Add.
-
Under the Getting Started section, select 2. Set up single sign on.
-
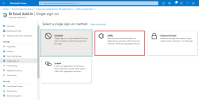
Select SAML for the single sign-on method.
Although there are 5 sections for the SAML SSO method, you only need to set the parameters in these sections:
Download the Azure Domain certificate from the SAML Signing Certificate section and use the Set up BI Web Server section as a reference for the mapping of terms from the SEI Installation Package. This is explained in further detail in Configuring the SEI Excel Add-in.
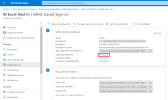
Basic SAML Configuration
-
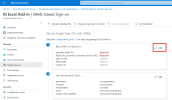
In the upper-right corner, click the pencil to edit the parameters in the Basic SAML Configuration section.
- In the Identifier (Entity ID) field, enter https://exceladdin/ followed by a Unique Identifier for your Azure Domain.
-
In the Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL) field, enter the value exactly as follows: https://exceladdin
-
Click Save to apply changes.
-
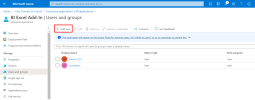
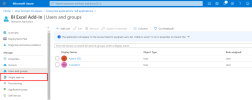
In the left menu, under the Manage section, click Users and groups.
-
In the upper bar, click + Add user to authorize users and groups to use SSO.
This completes the basic SAML configuration.
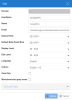
User Attributes & Claims
The installation package for the configuration of the SEI Excel Add-in application automatically fills in the ssoNameAttribute parameter with the USERNAME attribute by default.
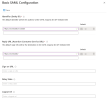
For the Azure Domain, you can replace this value with one of the attributes listed in the User Attributes & Claims section.
If you want to use the mailnickname attribute (because you want to choose the part of the email address before the @ sign), you will have to create it, since this attribute does not exist by default in the Azure Domain.
To create the attribute:
-
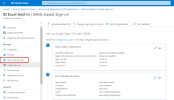
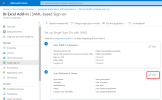
In the left menu, under the Manage section, click Single Sign-On.
-
In the upper-right corner, click the pencil to edit the User Attributes & Claims section.
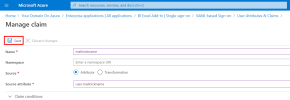
- Click + Add new claim.
- In the Name field, enter mailnickname.
- For the Source, select Attribute.
-
In the Source attribute field, enter user.mailnickname.
-
Click Save to finish.
Configuring the SEI Excel Add-in
Retrieving the Azure Certificate
Before starting the Excel Add-in configuration, you must retrieve the certificate from Azure Domain.
To retrieve the certificate:
- Scroll to the SAML Signing Certificate section.
-
Click Download next to the Certificate (Base64) field.
Editing the EXCEL.EXE.config file
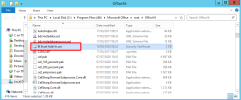
In order to fully benefit from Azure SSO functionality, you need to edit the EXCEL.EXE.config file.
You can find this file in these locations:
| Path | Office Version |
|---|---|
|
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\OfficeXX\ OR C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Root\OfficeXX\ |
32-bit |
|
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\OfficeXX\ OR C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Root\OfficeXX\ |
64-bit |
If you cannot find the EXCEL.EXE.config file in these locations, perform a search in the following directories depending on the Office version you are using:
-
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office for the Office 32-bit version
-
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office for the Office 64-bit version
| Attribute in EXCEL.EXE.config file | Value before change | Value after change | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| ssoMode | "None" | "Saml2" | Enable the SAML2 Single Sign-On mode |
| ssoSpEntityId | "https://exceladdin/SomeEntityId" | "https://exceladdin/ssoaddin" | Modify with the value entered in the Identifier (Entity ID) field according to your choice in Basic SAML Configuration |
| ssoSpReturnUrl | "https://exceladdin/" | "https://exceladdin/" | Should never be modified |
| ssoServiceAddress | "http://localhost:4504" | "http://yourserver:4504" | Modify according to your BI Service address |
| ssoWebURL | "http://localhost:81" | "http://yourserver:81" | Modify according to your Web Client address |
| ssoNameAttribute | "USERNAME" | "USERNAME" | Modify according to your choice in User Attributes & Claims |
| ssoDefaultCentralPoint | "\\SERVER\CentralPoint" | "\\YOURSERVER\CentralPoint" | Modify according to your Central Point shared folder path |
| ssoIdpEntityId | "https://stubidp.sustainsys.com/Metadata" | "https://sts.windows.net/c2c50f21-66a7-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/" | This is the value you retrieved from the Azure AD Identifier field in the Set up BI Web Server section |
| ssoModeSignOnURL | "https://stubidp.sustainsys.com/" | "https://login.microsoftonline.com/c2c50f21-66a7-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/saml2" | This is the value you retrieved from the Azure Login URL field in the Set up BI Web Server section |
| ssoSigningCertificateFileName | "stubidp.sustainsys.com.cer" | "BI Excel Add-In.cer" | For the Full certificate name field, enter the name of the certificate you downloaded from the Azure Domain with the .cer extension (for example: BI Excel Add-in.cer). |
Steps after the Installation/Configuration
Copying the Azure Domain Certificate
-
Copy the certificate you downloaded from the Azure Domain and paste it into your Office Excel folder (refer to Editing the EXCEL.EXE.config file for more details regarding the location).
Creating Users and Groups in SEI
-
Refer to Users to create your Web Client. Enter the same values for User Name and ssoNameAttribute you defined during the configuration of your EXCEL.EXE.config file.
Accessing SEI Excel Add-in with Azure SSO enabled
If you need to change a user connected with Single Sign-on, close Excel and clear your Internet Explorer 11 cache (refer to Internet Explorer & Microsoft Edge). This step is only required for Internet Explorer, as it is a Windows component and can access Windows cache. Other Web Browsers use their own cache.